|
Rotterdam
KLINGER The NetherlandsNikkelstraat 2 3067 GR Rotterdam
Elsloo
KLINGER Service Center LimburgBusiness Park Stein 208A 6181 MB Elsloo
Velsen-Noord
KLINGER The NetherlandsRooswijkweg 200 1951 MD Velsen-Noord
Moordrecht
Hadro TechnologySouth Lane 351 2841 MD Moordrecht |
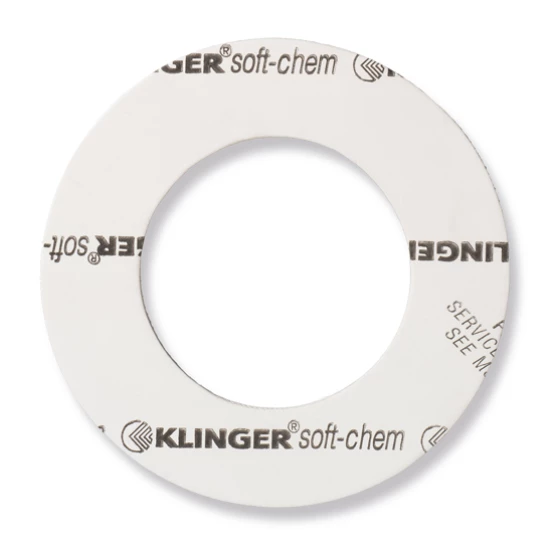
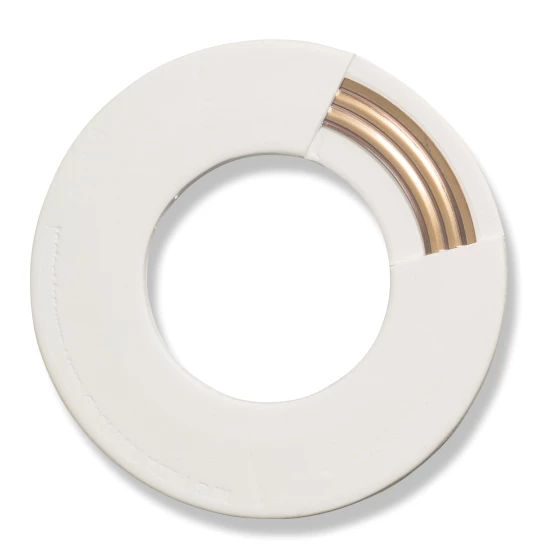
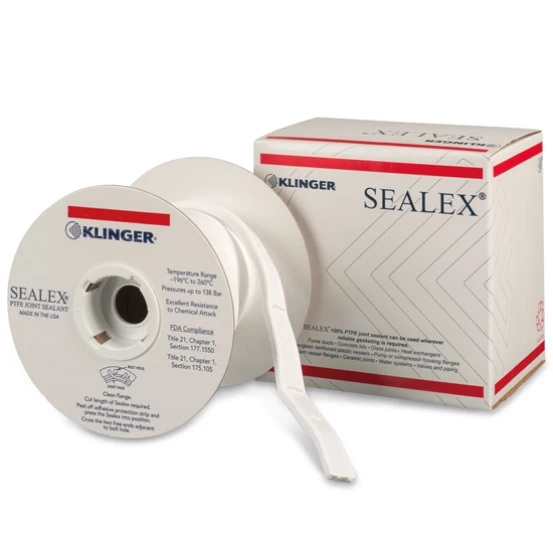
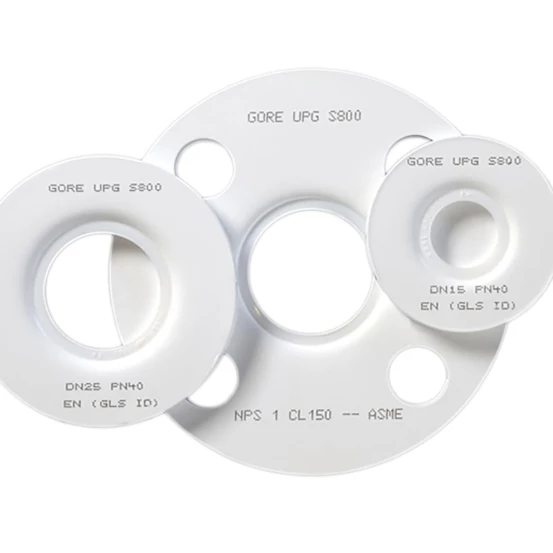
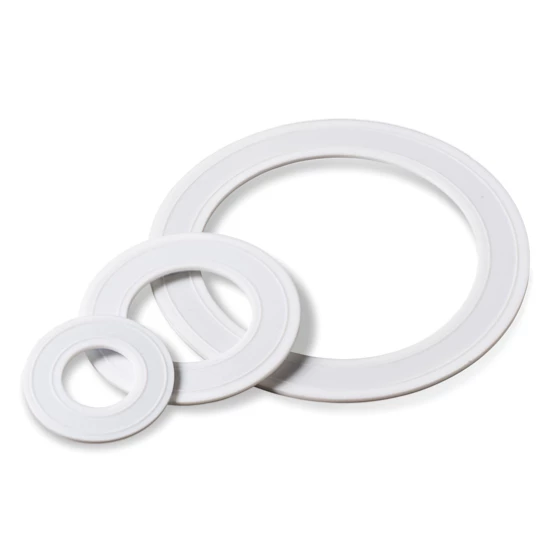
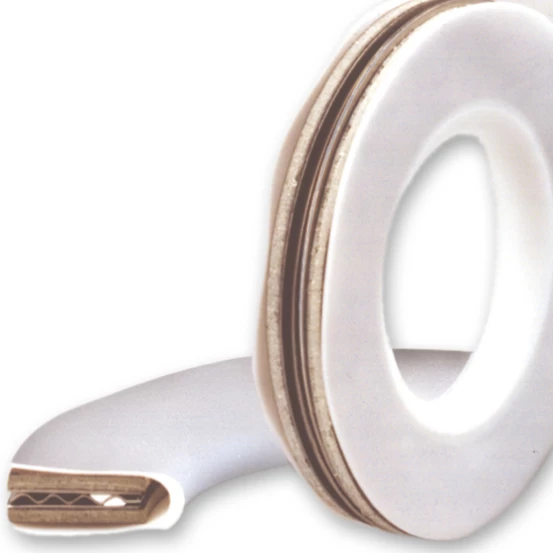
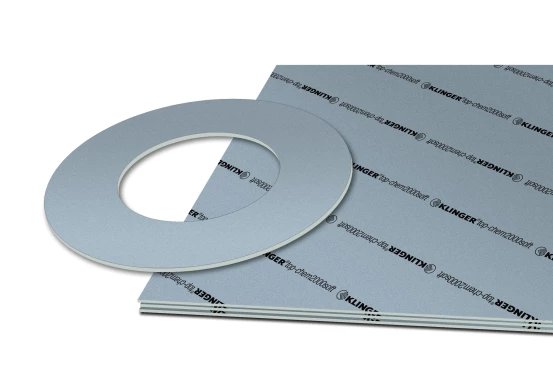
Product range: PTFE gaskets
PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) gaskets are high-quality seals known for their excellent chemical resistance and long service life. These properties are ideal for use in aggressive chemical environments, such as in the chemical industry and when transporting acids, bases and solvents.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
What is PTFE?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a plastic characterized by an exceptionally low coefficient of friction. It exhibits a high resistance to chemical reactions and boasts a melting point of 327º Celsius, making it suitable for a wide range of applications requiring heat and chemical resistance.
Is a PTFE gasket suitable for highly corrosive materials?
PTFE gaskets offer the advantage of being chemically inert and highly resistant to corrosion, making them virtually impervious to a wide range of acids, alkalis, and corrosive substances in environments up to 260º Celsius. This exceptional resistance significantly reduces the likelihood of chemical degradation or "attack" on the gasket, ensuring reliable performance even in harsh industrial settings.
What types of PFTE gaskets does KLINGER supply ?
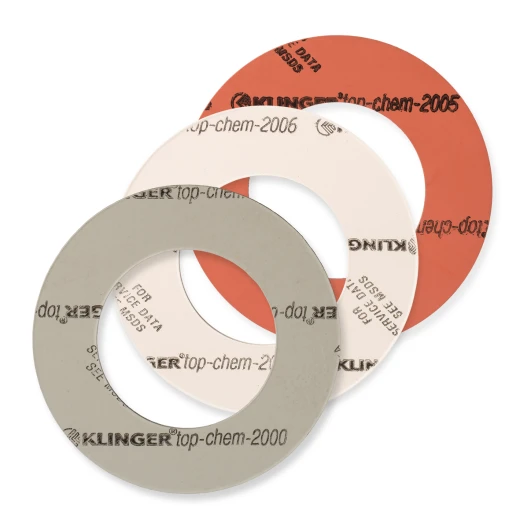
KLINGER offers a diverse range of gaskets including: KLINGER®TOP-CHEM 2000, KLINGER®TOP-CHEM 2003, KLINGER SOFT-CHEM, LOAD LOCK, KLINGER®TOP-CHEM 2005, KLINGER®TOP-CHEM 2006, PITA® DNA™, and KLINGER KEMPCHEN PW1A-3.
How are PTFE gaskets made?
In simple terms, PTFE seals undergo a baking process, which requires careful attention. When a block of PTFE is pressed flat, it tends to flow out similar to rubber, which is not ideal for sealing purposes as it loses its shape, rendering it unusable for flange connections. However, by incorporating a filler, the shape of the seal remains intact. This addition significantly reduces the impact of external forces on the deformation of the PTFE material.
Contact
For more information about our PTFE gaskets, please contact us at: